Slot Waveguide Modulator
Nonlinear polymer-clad silicon slot waveguide modulator with a half wave voltage of 0.25 V
By integrating a dual-layer graphene h-BN heterostructure on the tri-slot waveguide, a high efficiency modulator is designed, which combines the advantages of high modulation efficiency (0.376 dB/μm), low insertion loss (0.01 dB/μm), large modulation bandwidth (0.13 THz) and low power consumption (0.128 pJ/bit). We report an all-dielectric electro-optic (EO) polymer/TiO 2 multilayer slot waveguide modulator with low optical insertion loss for high-speed operations. The EO polymer is sandwiched between thin TiO 2 slot waveguide films to improve mode confinement in the EO polymer. The structure increased the mode confinement in the TiO 2 and EO polymer slot layers and reduced the electrode. The signal modulation for a slot-waveguide modulator with a 30 μm length is 4.8 dB and the modulation strength is notably improved to 0.16 dB/μm. This result implies that a 3 dB modulator can be achieved with a 20 μm nonresonant waveguide-based device, while offering a broad- band operation range (see Supporting Information). The Fermi-Dirac distribution. We also find that performance scales with modal waveguide confinement. Thus, we find highest energy-bandwidth-ratio modulator designs to be graphene, QD, QW, or 2D material-based plasmonic slot waveguides where the electric field is in-plane with the switching material dimension. We show that this improvement always. We report on an electro-optic modulator fabricated from a silicon slot waveguide and clad in a nonlinear polymer. In this geometry, the electrodes form parts of the waveguide, and the modulator driving voltage drops across a 120nm slot. As a result, a half wave voltage of 0.25V is achieved near 1550nm. This is one of the lowest values for any modulator obtained to date. As the nonlinear.
Abstract
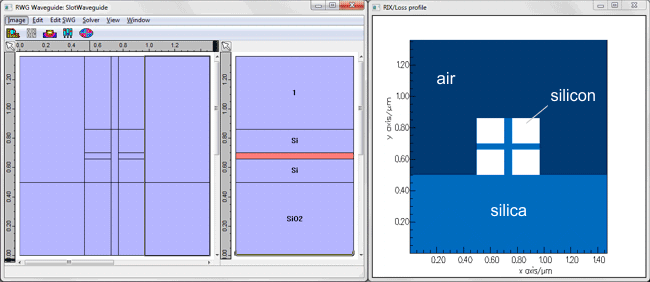
We report on an electro-optic modulator fabricated from a silicon slot waveguide and clad in a nonlinear polymer. In this geometry, the electrodes form parts of the waveguide, and the modulator driving voltage drops across a 120nm slot. As a result, a half wave voltage of 0.25V is achieved near 1550nm. This is one of the lowest values for any modulator obtained to date. As the nonlinear polymers are extremely resistive, our device also has the advantage of drawing almost no current, suggesting this type of modulator could operate at exceedingly low power.
- 42.65.Wi;
- 42.70.Jk;
- 42.79.Hp;
- 42.82.Et;
- Nonlinear waveguides;
- Polymers and organics;
- Optical processors correlators and modulators;
- Waveguides couplers and arrays
- Optics Letters
- Vol. 41,
- Issue 11,
- pp. 2501-2504
- (2016)
- •https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.41.002501
- Share
- Get CitationCopy Citation TextAbhijeet Phatak, Zhenzhou Cheng, Changyuan Qin, and Keisuke Goda, 'Design of electro-optic modulators based on graphene-on-silicon slot waveguides,' Opt. Lett. 41, 2501-2504 (2016)Export Citation
Abstract
We present a graphene-on-silicon (GoS) suspended vertical slot waveguide. By changing the Fermi level of graphene, the variation in the effective refractive index (RI) of the waveguide is a factor of two larger than that in the traditional GoS rib waveguide. The improvement is due to the light-intensity enhancement and the poor confinement of the optical mode in the slot nanostructure. We design Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) and microring modulators based on the GoS suspended vertical slot waveguide. Our calculations show that the modulators can be energy-efficient and footprint-compact due to the large phase shift of the propagating mode in the waveguide after applying a gate voltage on the graphene. Fabrication of our design is easy and CMOS-compatible. It paves the way for chip-integrated electronic-RI modulators.
© 2016 Optical Society of America
Full Article PDF ArticleOSA Recommended ArticlesDesign of graphene-on-germanium waveguide electro-optic modulators at the 2μm wavelengthJiaqi Wang, Qiuxia Li, Dan Huang, Chongbin Liang, Yuzhi Chen, Lin Fang, Youfu Geng, Xueming Hong, and Xuejin Li
OSA Continuum 2(3) 749-758 (2019)
Hai Yan, Xiaochuan Xu, Chi-Jui Chung, Harish Subbaraman, Zeyu Pan, Swapnajit Chakravarty, and Ray T. Chen
Opt. Lett. 41(23) 5466-5469 (2016)
Zhaolin Lu and Wangshi Zhao
J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(6) 1490-1496 (2012)
References
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Citation lists with outbound citation links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription

Cited By
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Cited by links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Figures (5)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Figure files are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Plate-slot Polymer Waveguide Modulator On Silicon-on-insulator
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Equations (7)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Equations are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Slot Waveguide Modulator Receiver
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Metrics
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Article level metrics are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Silicon Slot Waveguide
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription